|
|
 |
| ............................................................. |
|
|
| ........................................................ |
| From
the Editor |
|
Editorial
A. Abyad (Chief Editor) |
........................................................
|
|
Original contribution/Clinical Investigation
Diabetes Mellitus
- Knowledge, Management and Complications: Survey
report from Faisalabad-Pakistan
Ijaz Anwer, Ahmad Shahzad, Kashmira Nanji, Farah
Haider, Muhammad Masood Ahmad
Alanine aminotransferase
indicates excess weight and dyslipidemia
Mehmet Rami Helvaci, Orhan Ayyildiz* Mustafa
Cem Algin, Yusuf Aydin, Abdulrazak Abyad, Lesley
Pocock
Comparative Analysis of Antimicrobial Peptides
Gene Expression in Susceptible/Resistant Mice
Macrophages to Leishmania major Infection
Hamid Daneshvar, Iraj Sharifi, Alireza Kyhani,
Amir Tavakoli Kareshk, Arash Asadi
Does
socio-economic status of the patients have effect
on clinical outcomes after coronary artery bypass
grafting surgery?
Forough Razmjooei, Afshin Mansourian, Saeed
Kouhpyma
Comparison of the uterine
artery Doppler indices during pregnancy between
gestational diabetes and diabetes mellitus and
healthy pregnant women
Nazanin Farshchian, Farhad Naleini, Amir Masoud
Jaafarnejhad,
Parisa Bahrami Kamangar
Survey single dose
Gentamicin in treatment of UTI in children with
range of 1 month to 13 years old in Jahrom during
2015
Ehsan Rahmanian, Farideh Mogharab,
Vahid Mogharab
Evaluation of control of
bleeding by electro cauterization of bleeding
points of amplatz sheath tract after percutaneous
nephrolithotomy (PCNL) in Jahrom Peymanieh hospital
during year 2015-2016
Ali Reza Yousefi , Reza Inaloo
Comparison of the three-finger
tracheal palpation technique with triple ID
formula to determine endotracheal tube depth
in children 2-8 years in 2016-2017
Anahid Maleki, Alireza Ebrahim Soltani, Alireza
Takzare, Ebrahim Espahbodi,
Mehrdad Goodarzi , Roya Noori
Effect of Sevoflurane
and Propofol on pulmonary arterial pressure
during cardiac catheterization in children with
congenital heart diseases
Faranak Behnaz, Mahshid Ghasemi , Gholamreza
Mohseni, Azim Zaraki
Population and Community Studies
Prevalence
and risk factors of obesity in children aged
2-12 years in the Abu Dhabi Islands
Eideh Al-Shehhi, Hessa Al-Dhefairi, Kholoud
Abuasi, Noora Al Ali, Mona Al Tunaiji, Ebtihal
Darwish
Study and comparison
of psychological disorders in normal students
and students with multiple sclerosis in Shahrekord
Neda Ardestani-Samani, Mohammad Rabiei, Mohammad
Ghasemi-Pirbalooti, Asghar Bayati, Saeid Heidari-Soureshjani
Comparative
study of self-concept, physical self-concept,
and time perspective between the students with
multiple sclerosis and healthy students in Shahrekord
Neda Ardestani-Samani, Mohammad Rabiei, Mohammad
Ghasemi-Pirbalooti, Asghar Bayati, Saeid Heidari-Soureshjani
Relationship
between Coping Styles and Religious Orientation
with Mental Health in the Students of the Nursing-Midwifery
Faculty of Zabol
Nasim Dastras, Mohsen Heidari Mokarrar, Majid
Dastras, Shirzad Arianmehr
Tuberculosis in Abadan,
Iran (2012-2016): An Epidemiological Study
Ali-Asghar ValiPour, Azimeh Karimyan, Mahmood
Banarimehr, Marzieh Ghassemi, Maryam Robeyhavi,
Rahil Hojjati,
Parvin Gholizadeh
Family Stability and Conflict
of Spiritual Beliefs and Superstitions among
Yazdi People in Iran: A Qualitative Study
Zahra Pourmovahed , Seyed Saied Mazloomy Mahmoodabad
; Hassan Zareei Mahmoodabadi ; Hossein Tavangar
; Seyed Mojtaba Yassini Ardekani ; Ali Akbar
Vaezi
A comparative
study of the self-actualization in psychology
and Islam
Simin Afrasibi, Zakieh Fattahi
The effectiveness
of cognitive - behavioral therapy in reducing
the post-traumatic stress symptoms in male students
survivors of earthquake in the central district
of Varzeghan
Sakineh Salamat, Dr.Ahad Ahangar, Robab Farajzadeh
Reviews
Effects and mechanisms
of medicinal plants on stress hormone (cortisol):
A systematic review
Kamal Solati, Saeid Heidari-Soureshjani, Lesley
Pocock
Comparing Traditional
and medical treatments for constipation : A
Review Article
Mohammad Yaqub Rajput
A review of anti-measles
and anti-rubella antibodies in 15- 25 year old
women in Jahrom City in 2011
Ehsan Rahmania , Farideh Mogharab, Vahid Mogharab
Review of percutaneous
nephrolithotomy in children below 12 years old
in Jahrom hospital, during 2010-2014
Ali Reza Yousefi , Reza Inaloo
Physical and
mental health in Islam
Bahador Mehraki, Abdollah Gholami
International Health Affairs
The Challenges of Implementation
of Professional Ethics Standards in Clinical Care
from the viewpoint of Nursing Students and Nurses
Saeedeh Elhami, Kambiz Saberi, Maryam Ban, Sajedeh
Mousaviasl, Nasim Hatefi Moadab, Marzieh Ghassemi
Cognitive Determinants
of Physical Activity Intention among Iranian Nurses:
An Application of Integrative Model of Behavior
Prediction
Arsalan Ghaderi, Firoozeh Mostafavi, Behzad Mahaki,
Abdorrahim Afkhamzadeh,
Yadolah Zarezadeh , Erfan Sadeghi
Effect of resilience-based
intervention on occupational stress among nurses
Hossein Jafarizadeh, Ebrahim Zhiyani, Nader
Aghakhani, Vahid Alinejad, Yaser Moradi
Education and Training
Calculation of Salaries
and Benefits of Faculty Members in the Ministry
of Health and Medical Education of Iran
Abdolreza Gilavand
The effect of education
on self-care behaviors of gastrointestinal side
effects on patients undergoing chemotherapy
Shokoh Varaei, Ehsan Abadi Pishe, Shadan Pedram
Razie, Lila Nezam Abadi Farahani
Creating and
Validating the Faith Inventory for Students
at Islamic Azad University of Ahvaz
Solmaz Choheili, Reza Pasha, Gholam Hossein
Maktabi, Ehsan Moheb
Creating
and Validating the Adjustment Inventory for
the Students of Islamic Azad University of Ahvaz
Homa Choheili, Reza Pasha, Gholam Hossein Maktabi,
Ehsan Moheb
Evaluating
the Quality of Educational Services from the
Viewpoints of Radiology Students of Ahvaz Jundishapur
University of Medical Sciences
Abdolreza Gilavand, Jafar Fatahiasl
An Investigation
of Psychosocial aspect of Iranian Nursing Students'
Clinical Setting
Mahsa Boozaripour , Zanyar Karimi, Sima Zohari
Anbohi, Amir Almasi-Hashiani, Fariba Borhani
Clinical Research and Methods
Comparison of the
Antibacterial Effects of Chlorhexidine Mouth
washes with Jaftex Mouth wash on Some Common
Oral Microorganisms (An in Vitro Study)
Ebrahim Babadi, Zahra Bamzadeh, Fatemeh Babadi
Study of the effect
of plasma jet on Fusarium isolates with ability
to produce DON toxins
Elham Galin Abbasian, Mansour Bayat, Arash chaichi
Nosrati, Seyed Jamal Hashemi, Mahmood Ghoranneviss
The comparison of
anti-inflammatory effect in two methods of topical
dexamethasone injection and topical application
of ginger alcoholic extract after removing mandibular
wisdom teeth
Sahar Zandi, Seyyed Muhammadreza Alavi, Kamran
Mirzaie, Ramin Seyedian, Narges Aria, Saman
Jokar
The effect of curcumin
on growth and adherence of major microorganisms
causing tooth decay
Leila Helalat, Ahmad Zarejavid, Alireza Ekrami,
Mohammd Hosein Haghighizadeh, Mehdi Shiri Nasab
|
|
Chief
Editor -
Abdulrazak
Abyad
MD, MPH, MBA, AGSF, AFCHSE
.........................................................
Editorial
Office -
Abyad Medical Center & Middle East Longevity
Institute
Azmi Street, Abdo Center,
PO BOX 618
Tripoli, Lebanon
Phone: (961) 6-443684
Fax: (961) 6-443685
Email:
aabyad@cyberia.net.lb
.........................................................
Publisher
-
Lesley
Pocock
medi+WORLD International
11 Colston Avenue,
Sherbrooke 3789
AUSTRALIA
Phone: +61 (3) 9005 9847
Fax: +61 (3) 9012 5857
Email:
lesleypocock@mediworld.com.au
.........................................................
Editorial
Enquiries -
abyad@cyberia.net.lb
.........................................................
Advertising
Enquiries -
lesleypocock@mediworld.com.au
.........................................................
While all
efforts have been made to ensure the accuracy
of the information in this journal, opinions
expressed are those of the authors and do not
necessarily reflect the views of The Publishers,
Editor or the Editorial Board. The publishers,
Editor and Editorial Board cannot be held responsible
for errors or any consequences arising from
the use of information contained in this journal;
or the views and opinions expressed. Publication
of any advertisements does not constitute any
endorsement by the Publishers and Editors of
the product advertised.
The contents
of this journal are copyright. Apart from any
fair dealing for purposes of private study,
research, criticism or review, as permitted
under the Australian Copyright Act, no part
of this program may be reproduced without the
permission of the publisher.
|
|
|
| November 2017
- Volume 15, Issue 9 |
|
|
Cognitive Determinants
of Physical Activity Intention among Iranian
Nurses: An Application of Integrative Model
of Behavior Prediction
Arsalan Ghaderi (1)
Firoozeh Mostafavi (2)
Behzad Mahaki (3)
Abdorrahim Afkhamzadeh (4)
Yadolah Zarezadeh (5)
Erfan Sadeghi (6)
(1) Student Research center, school of health,
Isfahan University of medical science, Isfahan,
Iran
(2) Department of Health Education and Promotion,
School of Health, Isfahan University of Medical
Sciences, Isfahan, Iran
(3) Department of Biostatistics, School of Health,
Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan,
Iran
(4) Department of Community Medicine, School
of Medicine, Kurdistan University of Medical
Sciences, Sanandaj, Iran
(5) Social Determinants of Health Research Center,
Kurdistan University of Medical Sciences, Sanandaj,
Iran
(6) Non-communicable Diseases Research Center,
Fasa University of Medical Sciences, Fasa, Iran
Corresponding Author:
Firoozeh Mostafavi,
Department of Health Education and Promotion,
School of Health, Isfahan University of Medical
Sciences,
Isfahan, IR Iran.
Tel: +98-3137922710,
Email: f_mostafavi@yahoo.com
|
Abstract
Introduction: Sedentary
lifestyle and physical inactivity is recognized
as a risk factor for various diseases.
Nurses have a special place among healthcare
team members, and their numerous roles
require nurses to have good physical fitness.
The present study aimed to determine cognitive
factors related to doing regular physical
activity among a sample of Iranian nurses
based on the integrative model of behavior
prediction (IMBP).
Methods:
This cross-sectional study was conducted
in 2016 on a sample of 418 nurses who
were working in medical teaching hospitals
in Isfahan and Sanandaj in Iran. Participants
were randomly selected proportionally
to staff size among different hospitals.
A structured questionnaire was applied
for collecting data and data were analyzed
by SPSS version 16 using correlations,
linear and logistic regression statistical
tests.
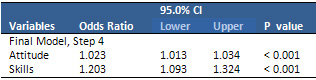
Results:
Mean age of the subjects was 33.1 years
(range, 21-53 years). 66.6%, 25.4%, and
8% had low, moderate, and severe physical
activity, respectively. The best predictors
for doing regular physical activity were
skills with OR of 1.203 [95% CI: 1.093,
1.324], and attitude with OR of 1.023
[95% CI: 1.023, 1.034]. The IMBP variable,
accounted for 34% of the variation in
the outcome measure of the intention to
do physical activity.
Conclusion:
Based on our result, it seems that
designing and implementation of educational
programs to increase attitude and skills
regarding doing physical activity may
be useful in the promotion of physical
activity.
Key words: Cognitive
Determinants, Physical Activity, Intention,
Nurses, IMBP
|
Nowadays one of the health problems is sedentary
lifestyle. In this regard, studies have shown
that more than 80 percent of people do not have
enough regular physical activity (1). The prevalence
of inactivity in urban and rural areas of Iran,
with an emphasis on leisure physical activities
between men and women in the age group of 15-64
years, was 76.3% and 55.8% respectively, with
the overall percentage of 67.6 percent (2).
Sedentary lifestyle and physical inactivity
is recognized as a risk factor for various diseases.
It is also raised as one of the main modifiable
risk factors for cardiovascular diseases and
plays an important role in the development of
other diseases (3). Researchers have shown that
adequate physical activity has a beneficial
effect on blood pressure, obesity and serum
lipids. So that, regular exercise is proven
to reduce total cholesterol, increase high-density
lipoprotein, reduce low-density lipoprotein,
and improve the general health of the body (4).
As a significant health promoting behavior,
regular physical activity can prevent or delay
the occurrence of chronic diseases and early
mortality (5). Nurses have a special place among
healthcare team members, and their numerous
roles require nurses to have good physical activity
(6). Nurses cannot meet the needs of patients
unless they pay great attention to the ways
of promoting their own lives and health (7).
Therefore, paying more attention to their health
condition and determining risk factors of nurses,
is very important (8). Studies have shown that
the most effective programs are theory-based,
rooted in social psychology (9, 10). Previous
research has also shown that psychological studies
and social psychology theories play an important
role in creating programs that impact on health
promotion. (11-17). The theories that examine
the role of these factors in predicting behavior
include the theory of rational action and the
theory of planned behavior (10). By developing
the theory of rational action and the theory
of planned behavior, Fishbein has proposed an
integrative model of behavior prediction in
which several factors such as attitude, subjective
norms, self-efficacy or perceived behavior control,
behavioral intention, skill, and environmental
constraints have been considered effective (18).
This research aims to find cognitive determinants
of physical activity intention among Iranian
nurses based on application of integrative model
of behavior prediction.
Participants
and
procedure
This
cross
sectional
study
was
a
part
of
a
project
conducted
among
Iranian
nurses
during
2016,
with
the
goal
of
providing
knowledge
for
the
promotion
of
physical
activity.
The
sample
size
was
calculated
at
95%
significant
level
according
to
the
results
of
a
study
by
Tofighi
et
al
(19)
which
reported
that
about
half
of
Iranian
nurses
were
lower
than
the
Average
levels
of
physical
activity
and
considering
the
20%
attrition
rate
(rate
of
drop-out
among
participants),
a
sample
of
418
was
estimated.
The
study
population
included
all
nurses
working
in
teaching
hospitals
in
Isfahan
and
Sanandaj.
In
this
study,
a
major
teaching
hospital
in
the
aforementioned
cities
was
randomly
selected
and
then
specifically-designed
questionnaires
were
distributed
among
nurses
who
volunteered
for
this
research
and
the
required
information
was
collected.
It
is
worth
mentioning
that
all
the
participants
were
informed
about
the
project
and
confidentiality
of
the
information,
as
well
as
the
purpose
of
the
project,
and
entered
the
study
with
consent.
All
questionnaires
were
anonymous
and
incomplete
questionnaires
were
excluded
from
the
study.
The
study
protocol
was
approved
by
the
institutional
review
board
and
ethics
committee
of
the
Isfahan
University
of
Medical
Sciences,
Isfahan,
Iran.
Measures
The
participants
were
instructed
about
how
to
fill
out
the
designed
self-report
questionnaire
before
gathering
the
required
information.
The
questionnaire
used
here
included
three
sections
including
demographic
information
questions,
integrative
model
of
behavioral
prediction
constructs,
and
the
short
form
of
the
international
physical
activity
questionnaire
(IPAQ).
A:
Demographic
Characteristics
Background
data
inquired
about
included
age,
gender,
marital
status,
education,
weight,
height,
waist
circumference,
record
of
membership
in
the
sports
club,
duration
of
membership
in
the
sports
club,
current
sport
club
membership
status,
and
job
history.
B:
IMBP
Variables
IMBP
items
were
designed
based
on
standard
questionnaires
applied
to
physical
activity
(20,
21).
Before
data
collection,
its
reliability
was
evaluated
using
the
alpha
coefficient
method
through
a
preliminary
study
on
30
cases
in
the
control
group.
This
questionnaire
consisted
of
the
constructs
of
attitude
(10
questions),
subjective
norms
(5
questions),
and
self-efficacy
(18
questions
-
Bandura’s
standard
physical
activity
self-efficacy
questionnaire
(22),
environmental
constraints
(10
questions),
skills
(4
questions)
and
behavioral
intention
(4
questions).
In
order
to
measure
the
score
of
each
construct,
the
mean
of
the
total
score
of
that
construct
was
considered.
Furthermore,
at
least
10
faculty
members
and
qualified
individuals
were
consulted
to
determine
the
validity
of
the
questionnaire
and
face
and
content
validity
were
determined.
In
order
to
determine
content
validity,
CVR
and
CVI
were
calculated
according
to
the
opinion
of
experts.
C:
Short
form
of
the
International
Physical
Activity
Questionnaire
(IPAQ)
This
questionnaire
asks
questions
about
the
amount
of
intense
and
moderate
physical
activity,
walking,
and
the
average
duration
of
sitting
over
the
last
week
(7
days).
Questionnaire
score
is
reported
according
to
the
IPAQ
protocol.
The
total
physical
activity
of
an
individual
per
week
is
measured
in
minute/week
–MET
format.
The
term
MET
refers
to
the
expression
metabolic
equivalent.
MET
is
a
unit
used
to
estimate
the
metabolic
cost
of
physical
activity.
One
MET
is
approximately
equal
to
the
amount
of
resting
energy
expenditure
for
an
individual
(23).
All
physical
activity
can
be
classified
with
multiples
of
resting
energy
expenditure.
The
questionnaire
includes
questions
about
the
physical
activity
of
participants.
This
section
can
be
finally
used
to
classify
physical
activity
into
three
categories:
Weak
or
low,
moderate,
and
severe.
This
questionnaire
has
been
used
by
the
World
Health
Organization
to
evaluate
the
level
of
physical
activity.
It
has
also
been
used
in
several
domestic
studies
and
its
validity
and
reliability
have
been
confirmed.
The
intensity
of
energy
expenditure
for
all
of
the
activities
during
the
past
7
days
was
calculated
according
to
IPAQ
instructions;
if
the
total
calculated
energy
during
the
week
is
600
to
3000
Met/Cal/Week,
the
intensity
of
the
activity
of
the
relevant
questionnaire
is
moderate
and
if
more
than
3000
Met/Cal/Week,
the
intensity
of
the
activity
of
the
relevant
questionnaire
is
severe.
Moreover,
if
the
amount
of
consumed
energy
is
less
than
600,
the
person
is
classified
as:
with
no
regular
physical
activity
(24).
Statistical
Analysis
Data
were
analyzed
by
SPSS
version
16
using
appropriate
statistical
tests
including
bivariate
correlations,
linear
and
logistic
regression
statistical
tests
at
95%
significant
level.
Mean
age
of
the
subjects
was
33.1
years
(range,
21-53
years).
Among
the
participants,
73.2%
were
female,
respectively,
among
whom
88
were
single,
268
married,
and
63
did
not
answer
the
marital
status
question.
Regarding
education,
90.9%
had
bachelor’s
degrees
and
9.1%
had
master’s
degree.
The
results
of
the
present
study
showed
that
66.6%,
25.4%,
and
8%
had
low,
moderate,
and
severe
physical
activity,
respectively.
Table
1
shows
the
Zero-order
correlations.
Statistical
significance
was
calculated
at
0.01
and
0.05.
The
results
showed
intention
was
correlated
with
the
attitude
(r=0.159),
subjective
norms
(r=0.222),
self-efficacy
(r=0.198),
skills
(r=0.553),
and
environmental
constraints
(r=0.128).
Environmental
constraints
was
significantly
correlated
with
self-efficacy
(r=0.130),
and
skills
(r=0.196).
In
addition,
skills
was
correlated
with
the
attitude
(r=0.143),
subjective
norms
(r=0.218),
and
self-efficacy
(r=0.147).
Furthermore,
self-efficacy
was
significantly
correlated
with
attitude
(r=0.133).
Finally,
subjective
norms
was
significantly
correlated
with
attitude
(r=0.136).
Click
here
for
Table
1:
Correlation
between
different
components
of
IMBP
Linear
regression
analysis
was
performed
to
explain
the
variation
of
physical
activity
intention.
As
can
be
seen
in
Table
2,
Collectively,
IMBP
variables
accounted
for
34%
of
the
variation
of
physical
activity
intention.
Table
2:
Predictors
of
the
intention
to
physical
activity
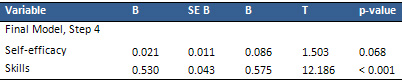
Adjusted
R
squared
=
0.34,
F:
80.190,
and
P
<0.001
However,
in
Table
3,
by
dividing
physical
activity
behavior
into
two
groups
of
people
without
physical
activity
(people
with
poor
physical
activity)
and
those
with
physical
activity
(people
with
moderate
and
severe
physical
activity)
and
using
logistic
regression,
it
was
observed
that
the
constructs
of
attitude
and
skill
were
more
important
regarding
physical
activity
behavior.
Table
3:
Multiple
logistic
regression
analysis
for
IMBP
components
related
to
physical
activity
| | |

